What Are Scaffold Shade Cloth and Scaffold Netting?
Scaffold shade cloth and scaffold netting are two important construction materials used on building sites in Australia. They serve as protective barriers to improve safety and working conditions during construction projects.
Scaffold Shade Cloth
Scaffold shade cloth is made from knitted polyethylene fabric designed to provide sun protection and reduce heat. It has a tightly woven construction that blocks different amounts of sunlight, creating cooler working environments for construction crews.
Scaffold Netting
On the other hand, scaffold netting has an open mesh design primarily used for keeping debris contained and preventing falls. It has a distinctive grid pattern that allows visibility while stopping objects from falling outside the construction area.
Key Differences
The main differences between these materials lie in their composition:
- Shade cloth uses dense knitted fibres to block UV rays effectively
- Netting is made of interwoven strands that create protective barriers without obstructing vision
Choosing the right material is crucial for ensuring worker safety, improving project efficiency, and meeting Australian construction standards. Your decision between scaffold shade cloth and scaffold netting will depend on specific site needs, environmental factors, and primary safety goals.
How Does Scaffold Netting Work?
Scaffold netting is a protective barrier used in construction sites. It is made of a strong mesh material called high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that is designed to be durable and long-lasting.
The main purpose of scaffold netting is to prevent objects from falling off scaffolding and causing accidents below. It achieves this by using an open weave construction that allows air to flow through while still being strong enough to catch any falling debris or tools.
Primary Functions of Scaffold Netting
The primary function of scaffold netting is to contain debris and protect workers on the construction site. Here are some specific things that scaffold netting can effectively capture:
- Falling tools and construction materials
- Dust particles and small debris
- Loose concrete fragments during demolition work
- Paint chips and surface materials during renovation projects
In addition to debris protection, scaffold netting also provides benefits for worker safety. It acts as a psychological barrier, helping to prevent accidental falls from scaffolding platforms. This means that site personnel can work with confidence, knowing that even if something were to drop, it wouldn’t endanger workers or pedestrians on the ground.
Visual Barriers and Perimeter Control
Another important function of scaffold netting is its ability to serve as temporary fencing around construction sites. This helps maintain security and control access to the area.
Scaffold netting provides visual screening for ongoing work, allowing people outside the site to see that there is construction happening without being able to see exactly what is going on. This can be useful for maintaining privacy or reducing distractions for nearby businesses or residents.
By using scaffold netting as a boundary marker, you can clearly establish where active construction zones are located and discourage unauthorised entry into those areas.
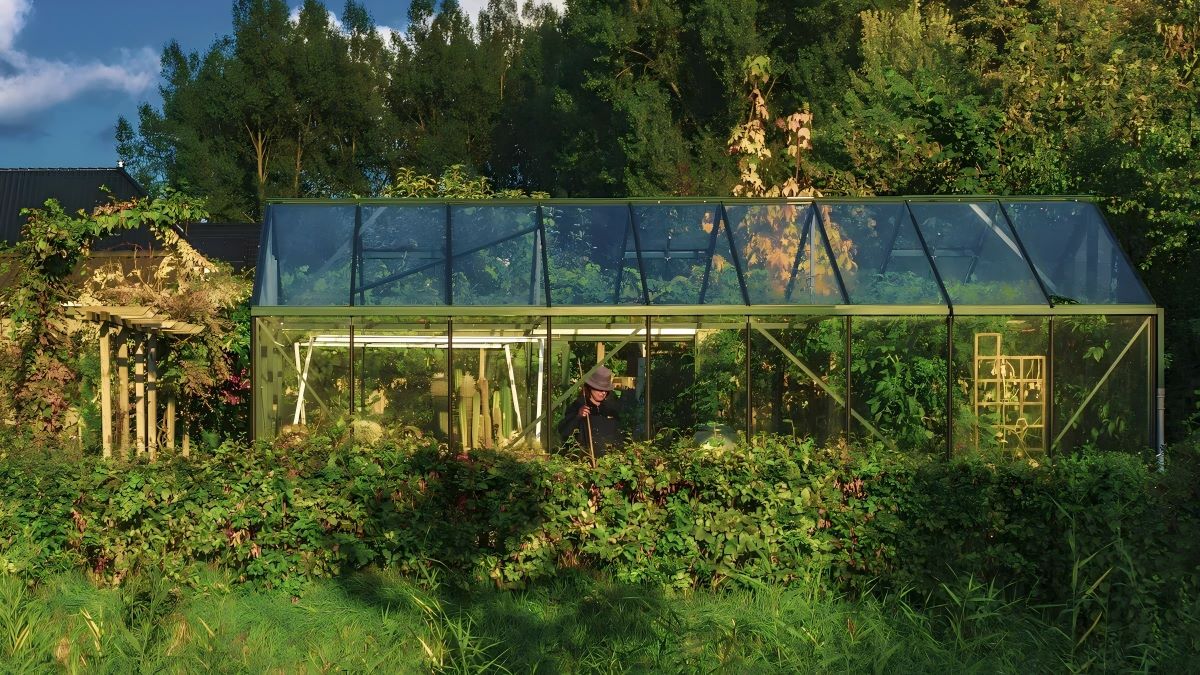
What Is the Purpose of Scaffold Shade Cloth on Construction Sites?
Scaffold shade cloth is a specially designed fabric made from knitted polyethylene. Its main purpose is to create comfortable working conditions on construction sites. This versatile material can transform harsh outdoor environments into manageable workspaces by significantly reducing heat exposure and providing essential weather protection for both workers and equipment.
The primary function of the fabric is to provide UV protection by blocking harmful solar radiation that can cause heat stress and decrease worker productivity. Construction teams working under direct sunlight often experience temperatures that can exceed safe working limits, making shade cloth an important safety investment rather than just a luxury addition.
Shade Factor Options and Their Impact
Scaffold shade cloth comes in three standard shade factors, each offering different levels of sunlight blockage:
- 30% shade factor – Provides light filtering while maintaining excellent visibility and airflow
- 50% shade factor – Delivers balanced protection suitable for moderate climate conditions
- 70% shade factor – Offers maximum sun blockage for extreme heat environments
The higher the shade factor percentage, the greater the reduction in solar heat gain. A 70% shade cloth can lower ambient temperatures by up to 10°C beneath the fabric, creating significantly more comfortable working conditions during peak summer months.
It’s important to choose the right shade factor based on your specific climate conditions, project duration, and the level of heat protection required for your workforce.
How Do Scaffold Shade Cloth and Scaffold Netting Differ in Terms of Material Construction?
The fabric types used in scaffold shade cloth and scaffold netting represent fundamentally different approaches to construction site protection. Scaffold netting employs an open mesh structure designed with larger openings that maintain visibility while containing debris. This construction allows air to flow freely through the material, preventing wind load buildup that could compromise scaffold stability.
Scaffold shade cloth utilises a tighter knit construction with smaller openings specifically engineered for sun blockage. The knitted polyethylene fibres create a denser weave pattern that blocks UV rays while still permitting controlled airflow. This mesh structure varies depending on the shade factor:
- 30% shade cloth: Looser weave with more open spaces
- 50% shade cloth: Medium-density construction balancing shade and airflow
- 70% shade cloth: Tighter weave providing maximum sun protection
The durability characteristics differ significantly between these fabric constructions. Scaffold netting’s open mesh design distributes stress across wider areas, making it exceptionally resistant to tearing from sharp debris or high winds. The material typically features reinforced edges and corner eyelets for secure attachment points.
Shade cloth construction prioritises UV resistance over impact protection. The knitted structure allows the material to stretch slightly under load, reducing stress concentration points. However, this flexibility means shade cloth requires different installation methods, often using tensioning systems rather than the rigid fixing points preferred for scaffold netting.
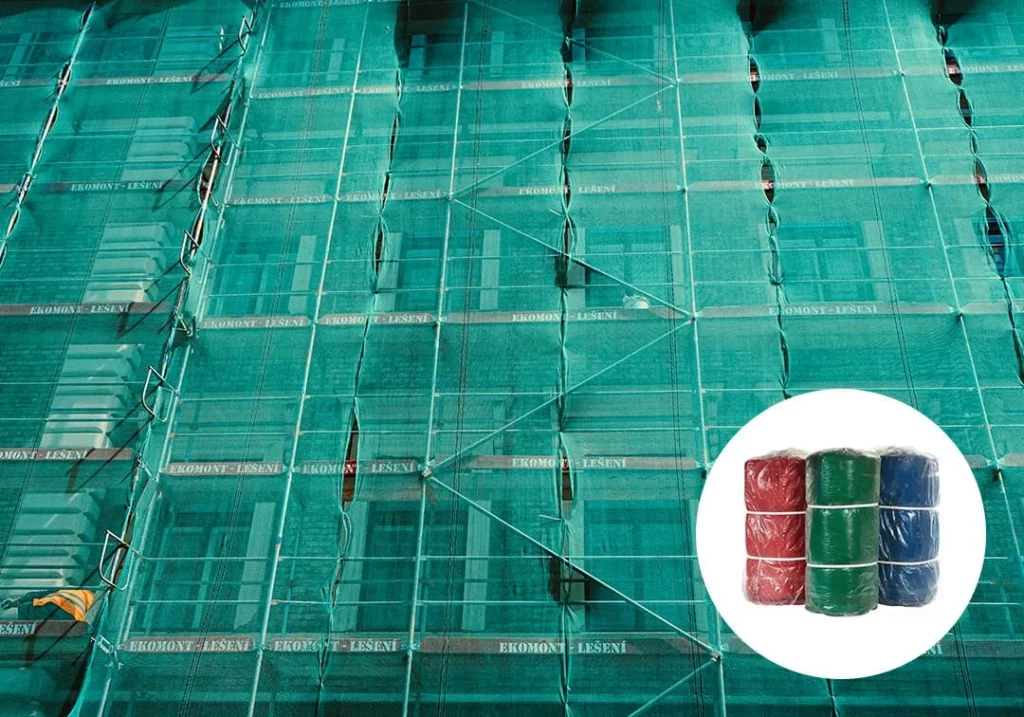

What Are the Key Safety Functions Served by Scaffold Netting and Shade Cloth?
Worker safety takes centre stage when comparing the protective capabilities of these two materials. Scaffold netting serves as your primary defence against falling debris, creating a robust barrier that catches tools, construction materials, and loose objects before they can injure workers below. The open mesh design allows you to maintain visual contact with work areas whilst providing essential containment for hazardous materials.
Dust containment represents another critical function where scaffold netting excels. Construction sites generate significant amounts of airborne particles, and the mesh structure effectively traps dust and small debris, protecting both your workforce and surrounding communities from respiratory hazards.
The safety profile differs considerably between these materials:
- Scaffold netting functions as a heavy-duty safety barrier designed to withstand impact from falling objects
- Structural integrity remains paramount, with reinforced edges and high tensile strength ratings
- Debris containment prevents materials from escaping the work zone
Shade cloth operates within a different safety paradigm, prioritising environmental comfort over physical protection. You’ll find its primary safety contribution lies in reducing heat-related health risks by creating cooler working conditions. The tighter weave blocks harmful UV radiation, helping prevent heat exhaustion and sunburn among your crew.
The material’s lighter construction means it cannot provide the same level of debris containment as scaffold netting, making it unsuitable for high-risk applications where falling objects pose significant threats to worker safety. However, it does play a role in eliminating certain risks associated with prolonged sun exposure.
When Should Construction Managers Opt for Scaffold Netting Over Shade Cloth?
Construction managers must prioritise scaffold netting when safety priorities demand robust debris containment systems. High-rise construction projects present the most compelling case for netting selection, particularly when working above pedestrian walkways or busy streets where falling objects pose severe injury risks.
In such scenarios, it’s crucial to consider alternatives like shrink wrap scaffolding which provide additional safety and protection.
Demolition and renovation projects require scaffold netting as the primary containment solution. These environments generate substantial debris volumes, including concrete fragments, metal pieces, and construction materials that standard shade cloth cannot effectively contain. You need the superior tensile strength and containment properties that only scaffold netting provides.
Regulatory compliance often dictates netting selection over shade cloth. Australian construction standards mandate specific debris containment measures for projects exceeding certain heights or located in high-traffic areas. Scaffold netting meets these stringent requirements whilst shade cloth typically falls short of compliance standards.
Consider scaffold netting for these specific scenarios:
- Multi-storey construction above 10 metres in urban environments
- Structural steel work where heavy components are lifted regularly
- Concrete cutting and drilling operations generating substantial debris
- Facade restoration projects involving material removal
- Wind-exposed sites where lightweight debris becomes projectile hazards
The mesh design of scaffold netting captures particles as small as 2mm whilst maintaining structural integrity under dynamic loads. You cannot achieve this level of protection with shade cloth, making netting the only viable option when worker and public safety take precedence over environmental comfort considerations. Read more about building laws and codes.
When Is It More Beneficial to Use Scaffold Shade Cloth Instead?
Weather protection needs become paramount when construction projects face extreme heat conditions. You’ll find scaffold shade cloth delivers superior performance in environments where worker comfort directly impacts productivity and safety outcomes.
Hot climate projects require strategic heat stress mitigation solutions. Construction sites in Australia’s northern regions or during peak summer months benefit significantly from shade cloth installation. The material’s knitted polyethylene construction creates cooling zones that reduce ambient temperatures by up to 10-15 degrees Celsius beneath the fabric.
Heat stress mitigation represents a critical safety consideration you cannot overlook. Workers exposed to prolonged direct sunlight face increased risks of:
- Heat exhaustion and dehydration
- Reduced concentration levels
- Decreased work efficiency
- Higher accident rates
Scaffold shade cloth addresses these concerns through its varying shade factors. You can select 50% shade cloth for moderate sun protection whilst maintaining good visibility, or opt for 70% coverage in extreme heat conditions.
Summer construction schedules particularly benefit from shade cloth deployment. The material allows continuous work during daylight hours when scaffold netting alone would leave workers vulnerable to harmful UV exposure. Construction managers report improved worker retention rates and reduced sick days when implementing comprehensive shade solutions.
Projects involving concrete work, roofing, or extended outdoor labour see immediate benefits from shade cloth installation, creating safer working environments without compromising site security.
Can Both Materials Be Used Together Effectively on a Single Construction Project?
Combined usage strategies deliver optimal results when you implement both scaffold netting and shade cloth across different zones of your construction site. You can position scaffold netting on high-risk areas where debris containment remains critical, whilst installing shade cloth over worker rest areas and equipment storage zones.
This dual approach maximises both safety and environmental comfort simultaneously. Your workers benefit from debris protection in active construction zones through scaffold netting, whilst enjoying temperature-controlled environments in break areas covered by shade cloth.
Strategic placement considerations include:
- Installing scaffold netting around perimeter scaffolding and demolition areas
- Positioning shade cloth over material storage zones and temporary offices
- Using netting for vertical protection and shade cloth for horizontal coverage
- Combining materials at different scaffold levels based on specific hazard profiles
You achieve comprehensive site protection when layering these materials according to risk assessment requirements. The investment in both materials proves cost-effective compared to potential injury claims or heat-related productivity losses. Your site supervisors can designate specific zones for each material type, ensuring workers understand which areas provide debris protection versus heat relief.

Conclusion
Making the right choice between scaffold shade cloth and scaffold netting—or using both materials together—directly impacts your construction project’s success. You need to evaluate your specific site conditions, safety requirements, and environmental challenges before making this critical decision.
Scaffold netting should be your primary choice when:
- Falling debris poses significant risks to workers and pedestrians
- You need robust containment solutions for dust and small materials
- Visual barriers around construction perimeters are essential
Scaffold shade cloth becomes the preferred option when:
- Heat exposure threatens worker comfort and productivity
- UV protection is crucial for extended outdoor work
- Environmental comfort takes priority over heavy-duty containment
You achieve optimal results by combining both materials strategically across different zones of your construction site. This approach ensures comprehensive protection whilst maintaining worker comfort throughout the project duration.
Remember that proper installation and regular maintenance of either material directly affects their performance. You should always consult with your safety officer and consider local regulations when implementing your strategy for maximum effectiveness.
Related : Using Plywood for Curved Concrete Forms: Techniques, Benefits & Modern Construction